Core Maps - Data Warehouse
Seamless Maps
Contents
Connecting to the Corporate GIS
Data Server
MLI Corporate GIS
Database Connection;
Data Layer Naming Convention
General
"ESRI provided" SDE ArcView Client Implementation Instructions Using the
Database Access Extension
Frequently asked questions
Connecting to the Corporate GIS Data Server
Connecting to the corporate live GIS data server, you must follow these few
simple instructions. Please make these modifications to the files listed below.
1. In the "HOSTS" file found in "C:\winnt\system32\drivers\etc\"
Add the following line:
10.140.37.238 gis2
2. In the "SERVICES" file found in
"C:\winnt\system32\drivers\etc\"
Add the following line:
esri_sde 5151/tcp # ESRI SDE Standard Instance port number
Once these additions have been made you will be able to gain access to the database.
For ArcView users be sure you download the latest "Database Access" Extension
from ESRI's Website for the version of ArcView You are using. Currently for ArcView 3.2
"Database Access" version is 2.1a. This link will provide you with proper patch
for your ArcView
http://www.esri.com/software/arcview/avsoftware.html
1. Be sure the "Database Access" Extension is loaded into ArcView.
2. From the "View" Menu choose the "Add Database Theme"
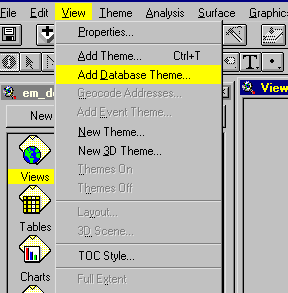
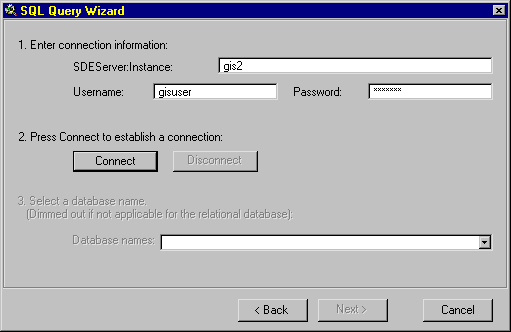
3. You will see the "SQL Query Wizard"
window, choose "Create a new connection"; "Using" SDE; Hit the
"Next" button.
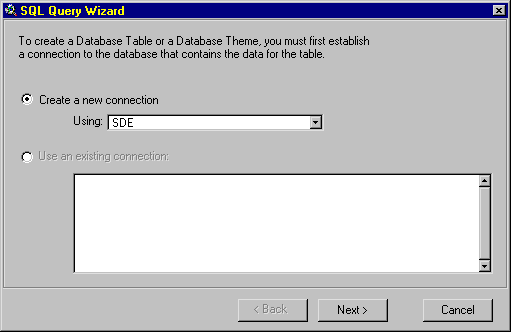
4. "SDE Server Instance" box enter: gis2
5. "Username" box enter: gisuser
6. "Password" box enter: gisuser
7. Hit the "Connect" button.
8. If a successful connection was made the "Connect" button will dim and the
"Next" button will be activated. Hit the "Next" button.
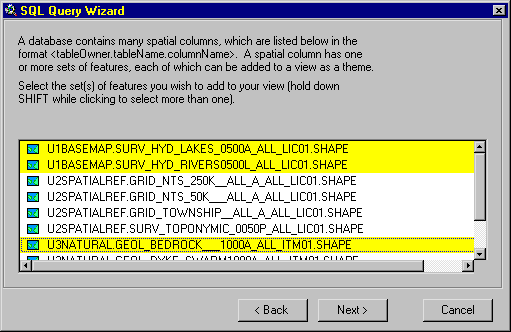
9. From the list of available data layers choose the layers you wish to load, you may
choose more than one layer by holding the "Shift" Key. Hit the "Next"
button.
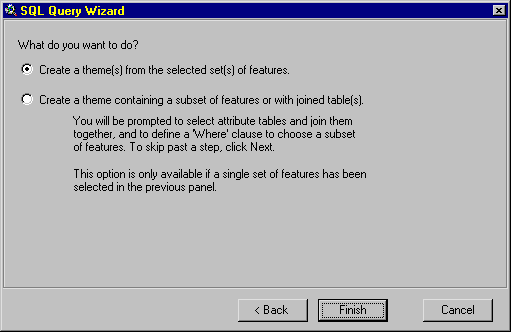
10. Choose your option from the radio buttons, the first choice is defaulted and hit
the "Finish" button to add your selected layers to your View.
Go to top
MLI Corporate GIS
Database Connection;
Go to top
Data Layer Naming Convention
The intent of this naming convention is to allow easy recognition of Spatial Data while
including some key Metadata in the layer name itself. Secondly the usage of this naming
standard is to allow easy access to data held in corporate geospatial databases (SDE/SDO).
Thirdly as a more precise reference to the data layer.
In the naming convention there are 7 distinctive sections of information provided in
the name. The full syntax is position sensitive and each section takes up a specified
number of characters. If all the characters are not required the field is padded to the
right hand side
|superclass__|bnch_layername_|scal|d|area_|dep|vn|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1) 5 Super classes of Data categorization (All GIS data must fall within one of these
categories).
chars:12
Options: NATURAL, BASEMAP, SPATIALREF, DEMOGRAPHIC, INFRASTRUC
2) The first 4 characters refer to departmental branch or major discipline followed by
a forced underscore (_) and then a free form description of the dataset in 10 characters.
E.g.. "SURV_HYDR_LAKE_" or "SURV_HYDR_RIVER"or
"GEOL_BEDROCK___"
chars:15
Options: free form field except for initial 4 characters to be branch name designation
or major dataset discipline.
3) The scale is based on a sliding decimal point with a base unit of 1:1000 represented
as "0001". Other options are:
1:1,000,000 = "1000"
1:100,000 = "0100"
1:10,000 = "0010"
1:1,000 = "0001"
1:100 = ".100"
1:10 = ".010"
1:1 = ".001"
Any Scale = "ALL_"
1:31,680 = "0031" We do loose the absolute scale here but this detail is
outside the purpose of this naming convention.
chars:4
Options: 1:9,999,000 = 9999 to 1:1 = .001
4) Data type in terms of GIS data options.
chars:1
Options: "R" = Raster, "P" = Point, "L" = Line,
"A" = Polygon or Area shape "T" = TIN (Triangulated Irregular
Network), "G" = Grid or Surface, "Z" = 3D Shape
5) Geographic reference based on the NTS Grid System.
chars:5
Options: "63K15" for 50k, "63K__" for 250k and "_ALL_"
for seamless provincial base dataset.
6) Government Departmental code based on reference given in the SHL e-mail listing.
chars:3
Options: "NR_" = Natural Resources, "EM_" = Energy and Mines,
"JUS" = Justice etc.
7) Version number starting at 01
chars:2
Options: "01" - "99"
Now to put it all together to make sense here are a few examples of the completed name,
please try these with a variety of datasets to see if there need to be adjustments.
NATURAL_____GEOL_BEDROCK___1000A_ALL_EM_01
BASEMAP_____SURV_HYD_RIVERS0500L63K15NR_04
General
"ESRI provided" SDE ArcView Client Implementation Instructions Using the
Database Access Extension
Before you can start working with SDE data in ArcView you need to find out some
information and make sure your machine is set up correctly. Find out who the SDE
administrator is in your organization, then arrange for some time to ask the following
questions.
Go to top
Frequently asked
questions
What is the name of the SDE server I'm connecting to?
The SDE server is the machine that has your data.
What is the name of the SDE database instance I'm connecting to?
The SDE database instance is the SDE process that lets you access
a set of spatial data.
What user name and password do I use to access the data?
?
Is my machine already set up to connect to SDE?
If your machine isnít already set up and you can do the work
yourself by following these instructions. You need to find out two things: the service
number of the SDE database instance, and the IP address of the SDE server.
Which tables in the database contain the data I want?
Which database contains the tables I need?
If you arenít familiar with the contents of the tables, ask for
a data dictionary. It is important to know which tables contain what data, how those
tables can be joined together, and what the column names in the tables mean.
Who do I contact if I can't connect to the database?
Sometimes you won't be able to connect to SDE because the SDE
server isnít running, or because of network problems. Make sure you can contact someone
to find out what is wrong and to have him or her solve the problem.
Before you can create database themes and database tables, find out if you have to set
up your machine. After following the instructions below, you should be able to connect to
SDE to create database themes and database tables.
Setting up your machine for SDE
To set up your machine for SDE you need to edit its Hosts and Services files. You can
do this in any text editor.
File Locations
Windows NT: <winnt root>\system32\drivers\etc
Windows 95: <win95 root>
UNIX: /etc
Services
This file must contain the SDE database instance name and its service number. For each
instance that you want to access, add the following line to the Services file:
<instance name> <service number>/tcp
For example, the default instance name is esri_sde and the default service number is
5150:
esri_sde 5150/tcp
Machines can be sensitive to the order in which entries appear in the services file. If
you have trouble connecting, try changing the order in which the SDE database instances
are listed.
Hosts
For each SDE server that you want to access, add the following line to the Hosts file:
<host name> <IP address>
For example,
stout 198.102.46.225
After editing the Hosts file, make sure you can 'ping' the SDE server. You can ping a
machine by typing "ping <host name>" at your prompt. You will be able to
connect if you get a reply from the server. If you don't get a reply, then you likely
spelled the server's name wrong or typed the IP address incorrectly in the Hosts file.
PCs only: If your PC doesn't have a Hosts file you must create a new one. A sample
Hosts file is often provided, called Hosts.sam. When saving the new Hosts file, some text
editors will automatically attach a .txt extension to it; rename the file to eliminate the
.txt extension. If you don't have a Ping utility to check communication with the server,
you need to open a DOS window.
Before you can start working with SDE data in ArcView, you need to find out some
information from your SDE database administrator.
To create database themes and database tables using data from an SDE database you first
need to connect to the SDE server. The database is case sensitive when evaluating the
strings you type in, so be sure you type them in correctly.
To connect to an SDE database server
1 Load the Database Access extension.
2 You make a connection to the database when you create a database theme or a database
table, or when you repair a database theme's or a database table's connection. In the
dialog you use for one these tasks, choose the Create a new connection option.
3 Choose the Create a new connection option. If you're using the SQL Query Wizard,
click Next; otherwise, click the Connect button to open the SDE New Connection dialog.
4 In the SDEServer:Instance text box, type the SDE server name and the database
instance name, separated by a colon, like <server>:<instance>. These two
pieces of information together define which SDE database you are connecting to. For more
information, see the note below.
5 In the Username text box, type your user name for accessing the SDE database.
6 In the Password text box, type your password for accessing the SDE database.
Together, your user name and password define your permissions in the SDE database.
7 Click Connect. You are connected to the database when the Connect button dims out.
8 Some relational databases contain several databases, or groups of related tables. If
the relational database used by SDE has databases of tables, a list of their names will
appear; otherwise, this step will be dimmed out. Choose the database containing the tables
you want to access, or skip to the next step.
9 Click Next or OK, whichever is present in the dialog you are connecting from.
You've finished making an SDE connection. Now you can create database themes and
database tables.
Note If the database instance uses SDE's default name, esri_sde, you only need to type
in the server name (without the colon). If the database instance does not use the default
name, you can set an environment variable called SDEINSTANCE to contain the instance name;
if this variable has been set, you only need to type in the server name (without the
colon).
How and when to use the Disconnect button
When the Connect button dims out, the Disconnect button becomes available. You can see
the contents of the database you're connected to in the database names list. If you look
at this list and realize that you've connected to the wrong SDE database, you can change
your connection by clicking Disconnect. When you click Disconnect, it dims out and Connect
becomes available. Change the contents of the text boxes to identify the correct SDE
database. Click Connect when you're done.
If you realize you've connected to the wrong SDE database after clicking OK or Next,
how you change the connection depends on which interface you are using:
If you're using the SQL Query Wizard and you've already clicked Next, you have two
choices. One option is to click Cancel, then open the SQL Query Wizard and start again.
The other option is to move back to the connection panel. Click Disconnect, then make a
new SDE connection. You will lose any choices you've made in the wizard.
If you're using the Add Database Table dialog and you've already finished creating a
connection with the SDE New Connection dialog, you need to make another new connection.
Choose the Create a new connection option, click the Connect button , then make a new SDE
connection.
When connections disappear from the existing connections list
ArcView only saves connections in a project if they are associated with a database
theme or a database table.
If you create a connection in the SQL Query Wizard or the Add Database Table dialog,
then click Cancel before creating a database theme or a database table, ArcView won't save
the connection in the existing connections list; the connection isn't associated with a
theme or a table.
If you delete from a project all the database themes and database tables that require a
connection, then the connection will be removed from the existing connections list.
If you create a database table, join that database table to a local ArcView table, then
delete the original database table, ArcView will save the connection required for the
joined attributes until you remove all joins from the local table. Then, if no themes or
tables require the connection, it will be removed from the existing connections list.
SDE data structure
SDE stores your spatial data in relational database tables. Your database has a
collection of tables, some of which may contain spatial data and others which do not.
Spatial data is stored in a spatial column of a table in the same way that numeric data is
stored in a numeric column. You can add a spatial column to any table in the database.
A collection of geographic features that share a common thematic subject should all be
stored together in one business table. There are no limitations to the kinds of features
one table can store, only that all features in a table must lie within a defined range of
coordinates. For example, you might have a business table containing all the hydrographic
features in Manitoba including lakes (polygon), rivers (line), aqueducts (line), dams
(point), and annotation for these features (anno). Each record in the business table is
not required to have a value in the spatial column; records can also contain SDE's null
feature type.
The business table could contain attributes such as the name of the feature, its depth
(if appropriate), the date it was created (if appropriate) and the type of feature it is.
Your database can have several other tables in the database containing attributes about
the features in a business table, including tables describing the levels of pollutants or
maintenance work, and lookup tables describing the features. These attribute tables can be
joined to the business table in a database theme's query.
ArcView and SDE feature types
Even though a business table can contain many classes of features, a database theme in
ArcView can represent only one of them: polygon, line, point, or anno.
When you create database themes using the SQL Query Wizard, you choose the spatial
column you want to see from a list of the spatial columns you can access. In that list, if
a spatial column has feature types from more than one ArcView class it will have a folder
icon. Click on the folder to choose the feature class your theme will represent. If you
select the name of a spatial column that has a folder icon without choosing a feature
class, ArcView makes a theme for the default feature class. ArcView decides which class is
the default by checking the feature types a spatial column can have; ArcView looks for
polygons, then for lines, then for points, and, lastly, for anno.
A spatial column that can have features from many classes may presently contain only
one class of features. For example, you will be able to create both polygon and line
themes from a spatial column that can have both polygons and lines even if it only
contains lines at that time. If you create a polygon theme, it will appear empty when you
draw it. Another person might be adding polygons, but hasn't yet committed the new
features to the database.
Each SDE feature type has specific rules about the geometry it represents. ArcView
shapes do not follow the same rules, and therefore are not always valid SDE features. You
may not be able to store some ArcView shapes in SDE.
Go to top |